What is a Planet?
An astronomical body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its
gravity,
is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of
planetesimals.
Mercury

- Day - About 59 Earth days (to complete one rotation on its axis)
- Solar Day - About 176 Earth days (one full day-night cycle)
- Year - 88 Earth days
- Planet Type - Terrestrial
- moon - 0
Venus
- length of Day - 243 Earth days
- Year - 225 Earth days
- Distance from Sun - 67 million miles (108 million kilometers)
- Planet Type - Terrestrial
- Moon - 0
- Surface temperature - 900° F (480° C)

Earth

- Day - 23.9 hours
- Year - 365.25 days
- Radius - 3,959 miles | 6,371 kilometers
- Planet Type - Terrestrial
- Moon - 1
Mars
- Day - 24.6 hours
- Year - 669.6 sols | 687 Earth days
- Planet Type - Terrestrial
- Radius - 2,106 miles | 3,390 kilometers
- Moon - 2 (Phobos, Deimos)

Jupiter
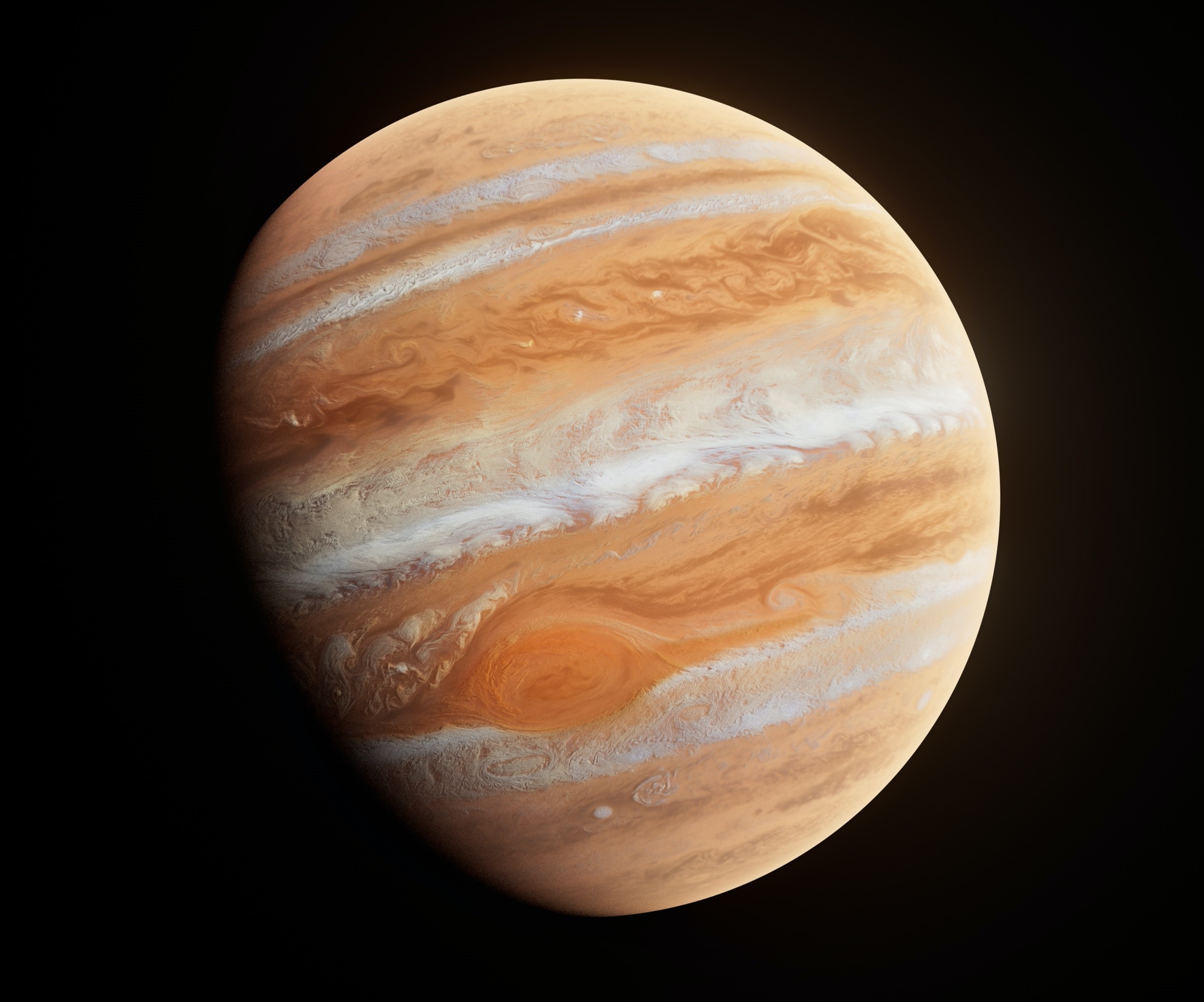

- Namesake - King of the ancient Roman gods
- Day - 9.93 hours
- Year - 11.86 Earth Years
- Distance from Sun - 5.1 Astronomical Units (Earth=1)
- Planet Type Gas giant
- Moons - 80
- Jupiter's four largest moons - Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto - were first observed by the astronomer Galileo Galilei in 1610
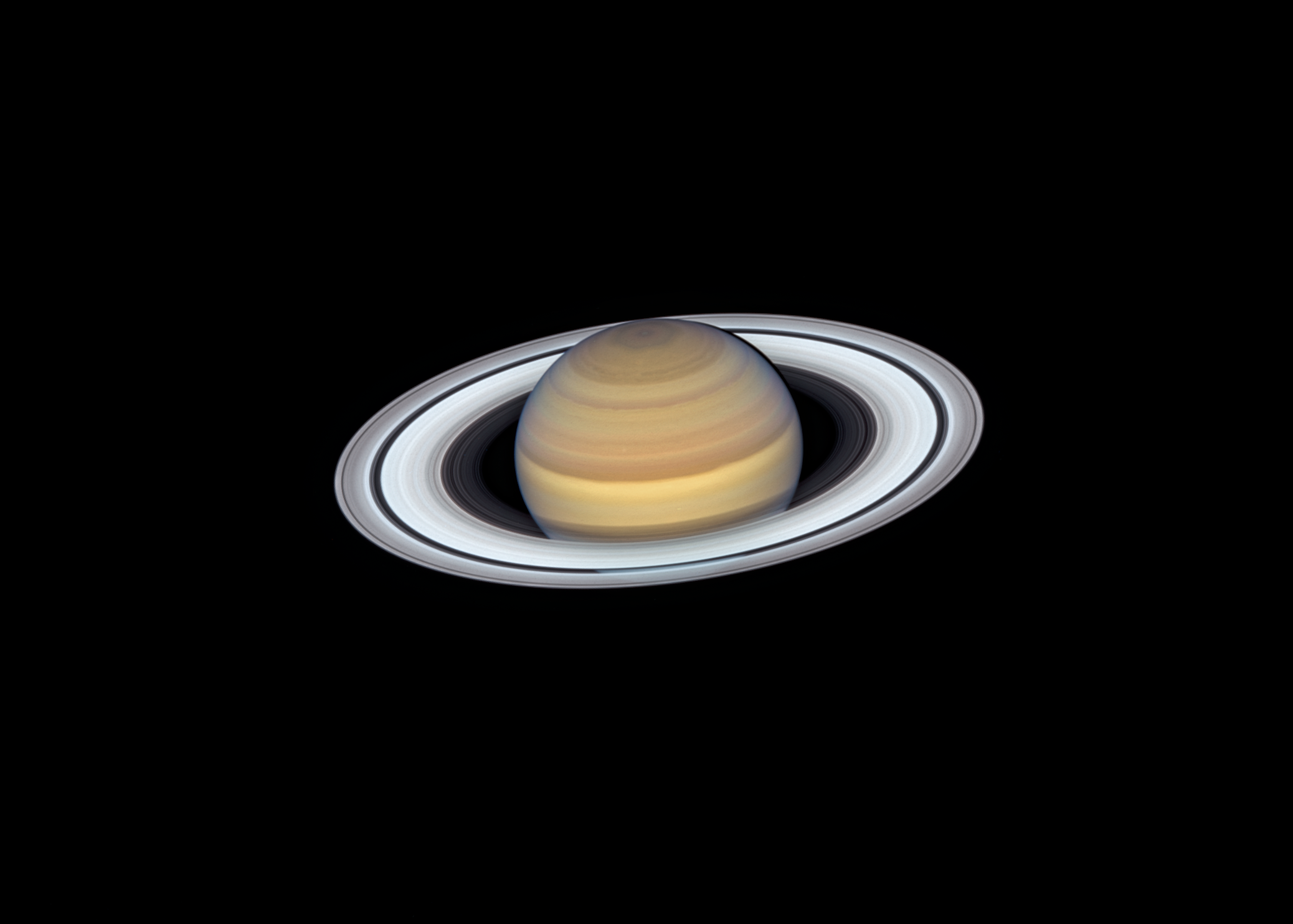
Saturn
- Day - 10.7 hours
- Year - 29 Earth Years
- Planet Type - Gas giant
- Radius - 36,183.7 miles | 58,232 kilometers
- Moons - 83
Uranus
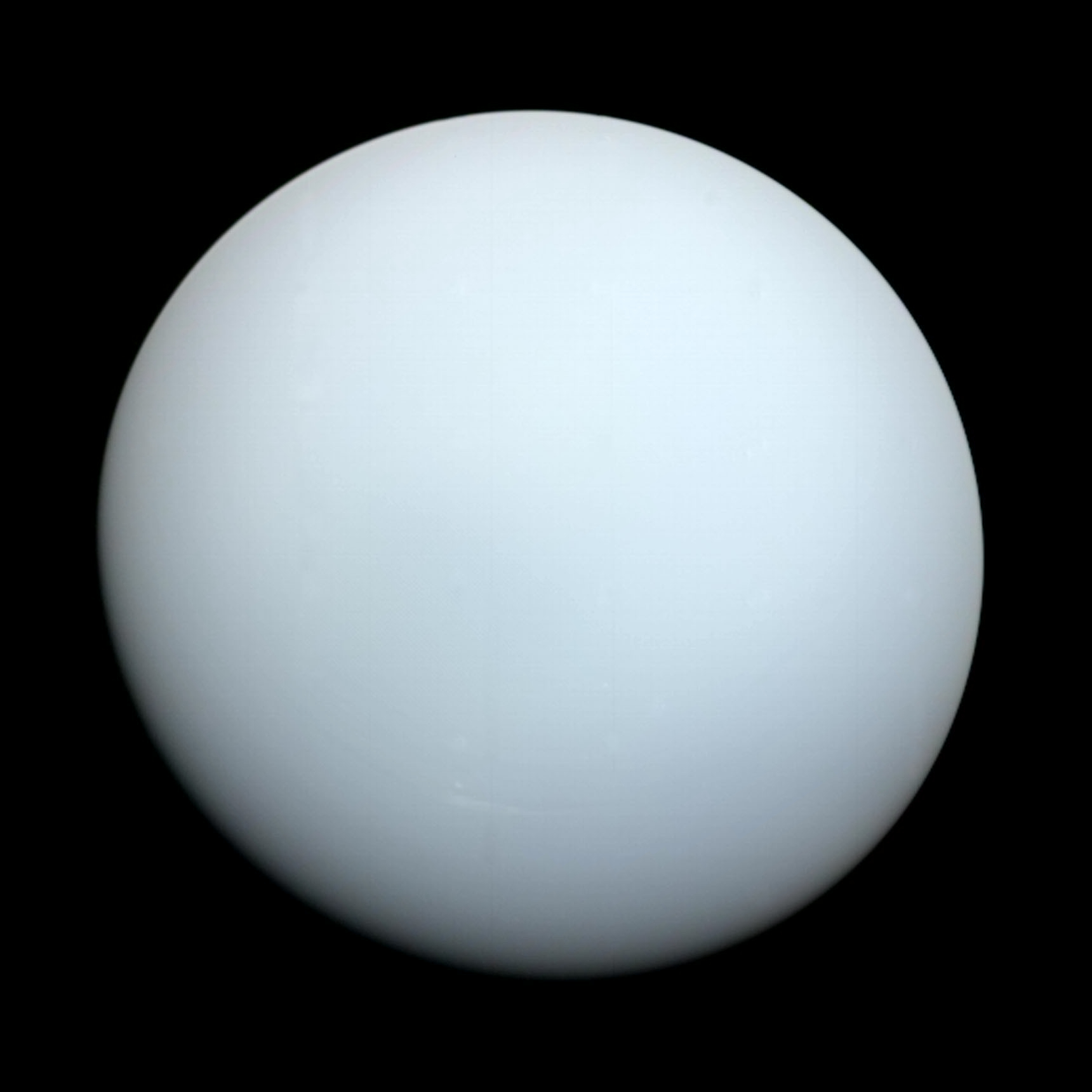

- Day - 17 hours 14 minutes
- Radius - 15,759.2 miles | 25,362 kilometers
- Year 84 Earth years
- Planet Type - Ice Giant
- Moons - 27
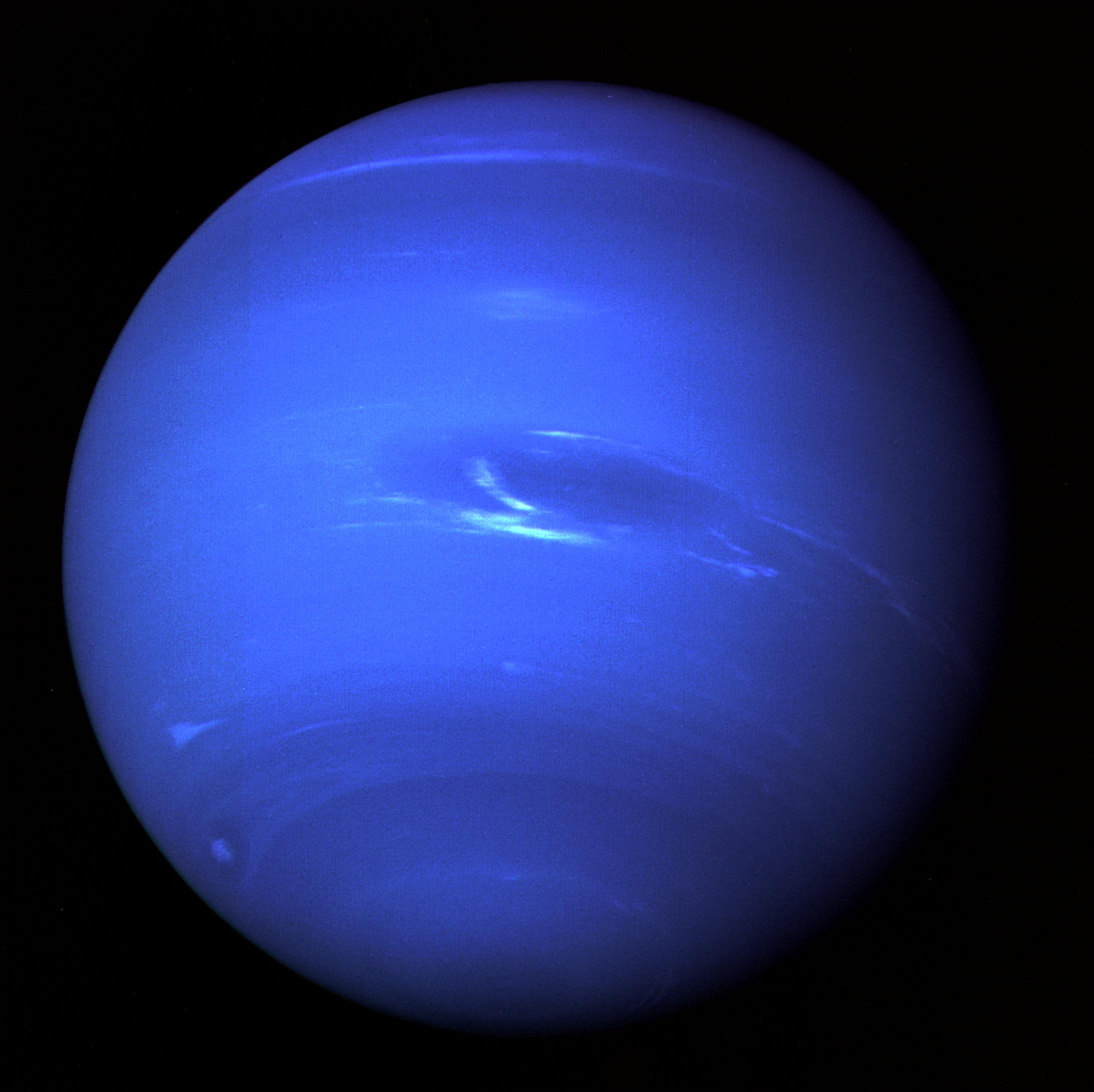
Neptune
- Day - 16 hours
- Radius - 15,299.4 miles | 24,622 kilometers
- Years - 165 Earth years
- Planet Type - Ice Giant
- Moons - 14
What is a Dwarf Planet?
According to the International Astronomical Union, which sets definitions for planetary science, a
dwarf planet is a celestial body that - orbits the sun, has enough mass to assume a nearly round
shape, has not cleared the neighborhood around its orbit and is not a moon.
Ceres
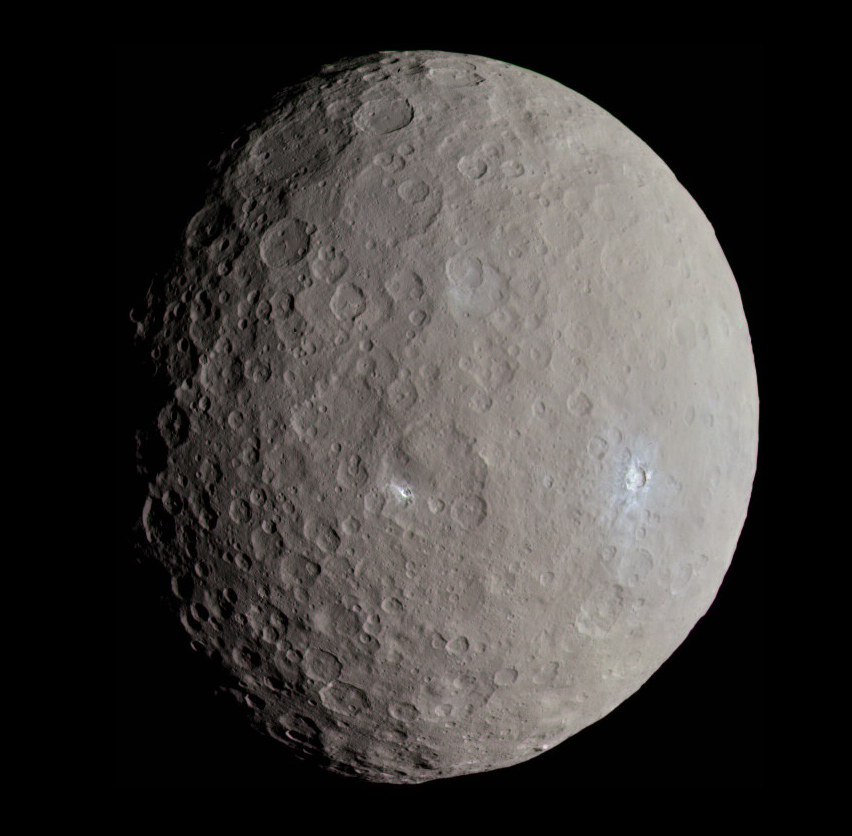

- Planet Type - Dwarf
- - Ceres comprises 25% of the asteroid belt's total mass
- NameShake - Ceres is named for the Roman goddess of corn and harvests. The word cereal comes from the same name.
- Day - Ceres takes 1,682 Earth days, or 4.6 Earth years, to make one trip around the Sun.
- Moon - 0
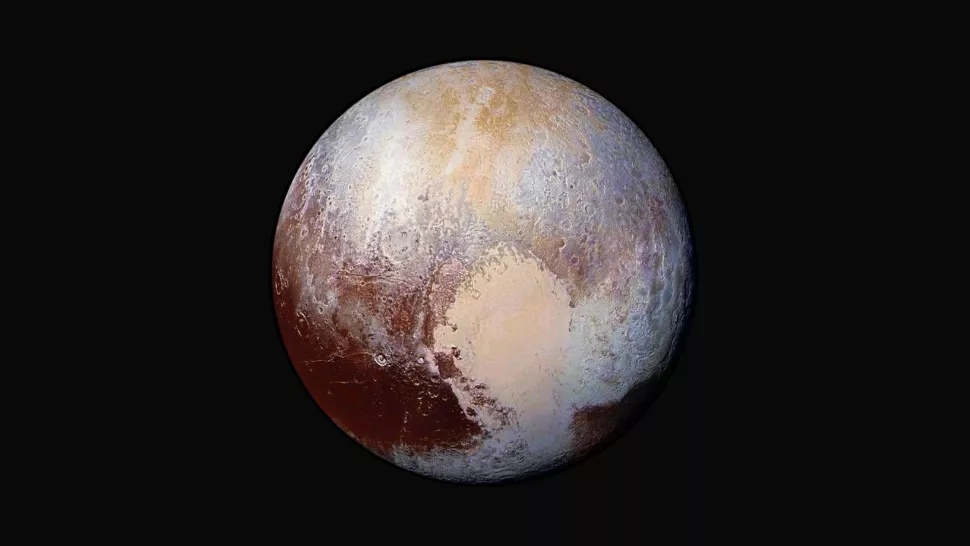
Pluto
- Day - 153 hours
- Year - 248 Earth years
- Planet Type - Dwarf
- Radius - 715 miles | 1,151 kilometers
- Moon - 5 (Charon, Hydra, Kerberos, Nix, Styx)

Eris

- Day - 25.9 hours
- Year - 557 Earth years
- Radius ~ 722 miles | 1,163 kilometers
- Planet Type - Dwarf
- Moon - 1 (Dysnomia)
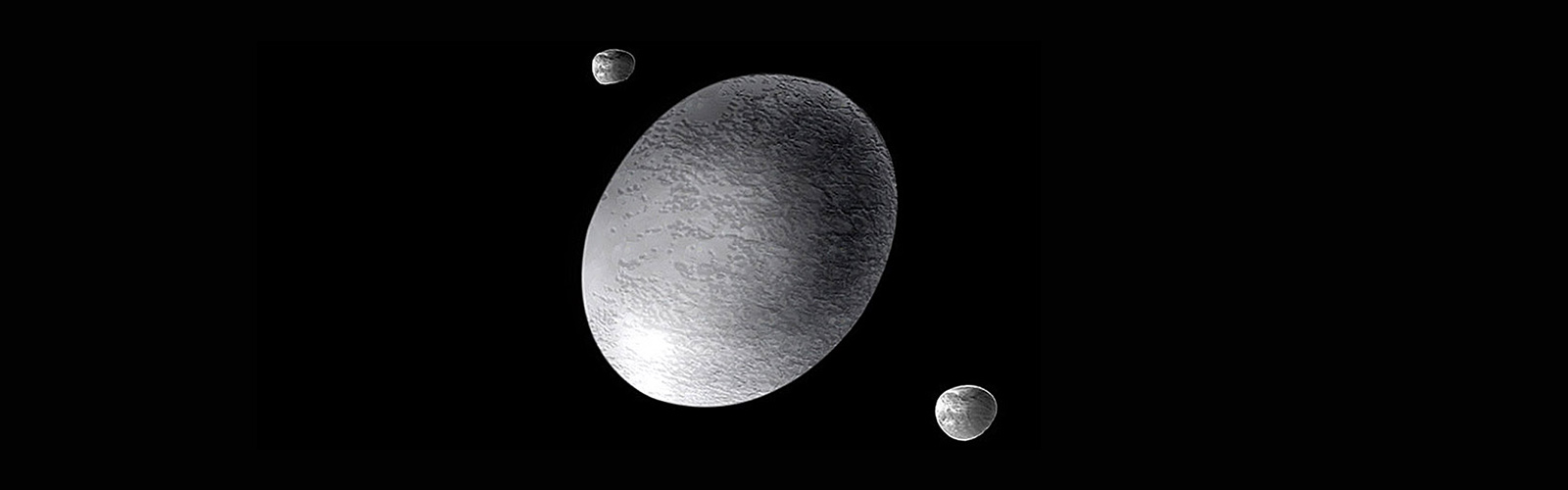
Haumea
- Day - 4 hours
- Year - 285 Earth years
- Planet Type - Dwarf
- Radius ~ 385 miles | 620 kilometers
- Moon - 2 (Namaka (inner moon), Hi'iaka (outer moon))

Makemake
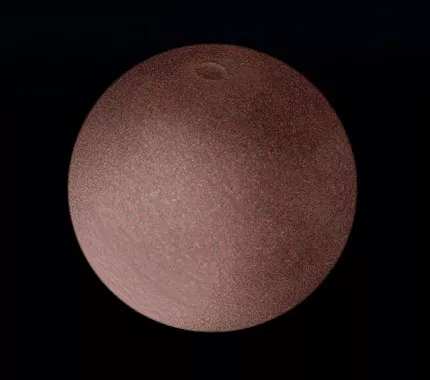
- Day - 22.48 hours
- Year - 305.34 Earth years
- Radius ~ 444 miles | 715 kilometers
- Planet Type - Dwarf
- Moon Confirmed - 0
- Moon Provisional - 1 (S/2015 (136472) 1, MK 2 Nicknamed )
What is International Space Station?
International Space Station (ISS), space station assembled in low Earth orbit largely by the United
States and Russia, with assistance and components from a multinational consortium.
The project, which began as an American effort, was long delayed by funding and technical problems.
Assembly of the International Space Station (ISS) began with the launches of the Russian control module Zarya on November 20, 1998, and the U.S.-built Unity connecting node the following month, which were linked in orbit by U.S. space shuttle astronauts.
Assembly of the International Space Station (ISS) began with the launches of the Russian control module Zarya on November 20, 1998, and the U.S.-built Unity connecting node the following month, which were linked in orbit by U.S. space shuttle astronauts.
ISS (International Space Station)
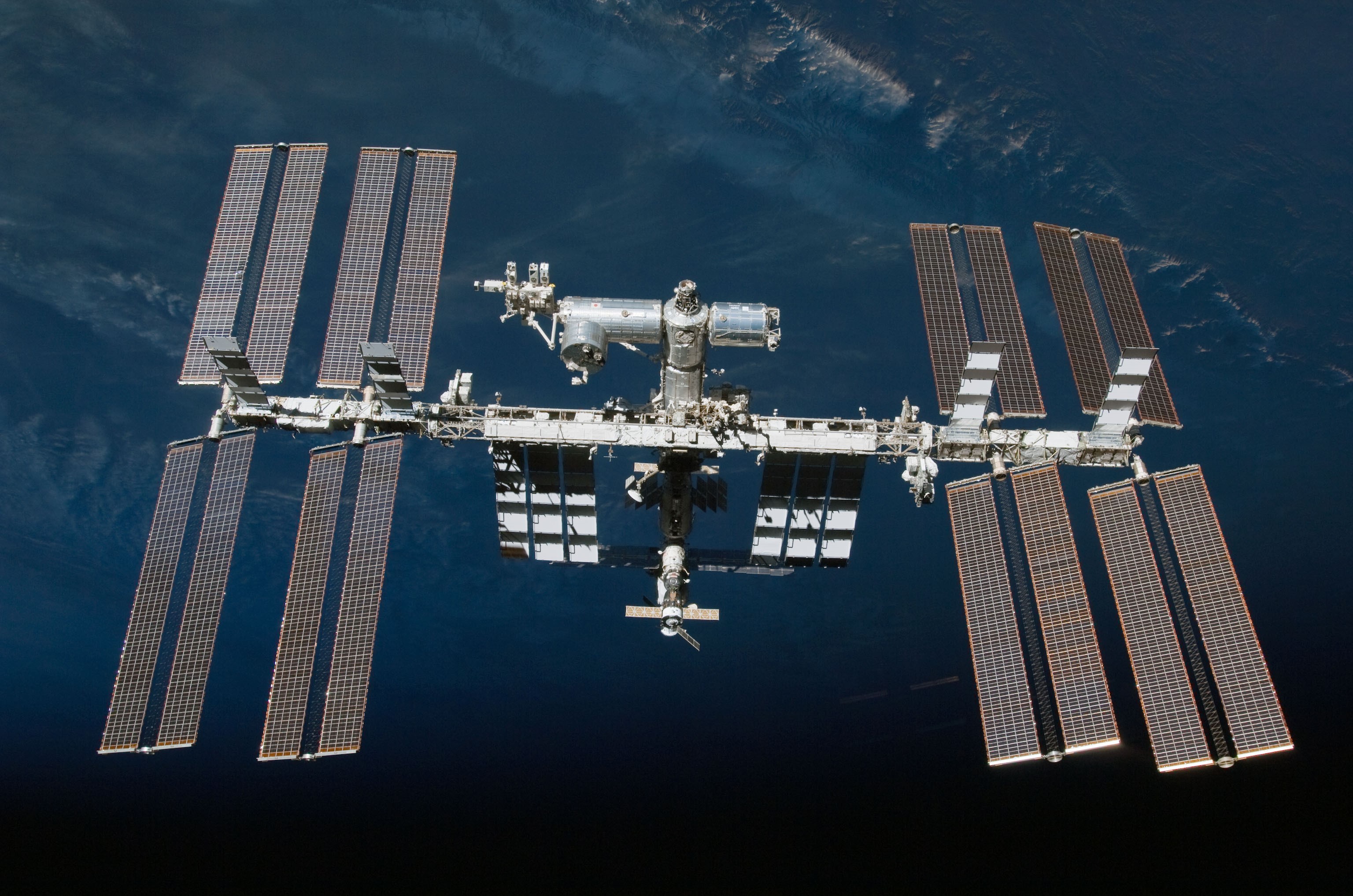

- - It orbits Earth at an average altitude of approximately 250 miles.
- - It serves as a home where crews of astronauts and cosmonauts live.
- Speed - It travels at 17,500 mph.
- Orbit - It orbits Earth every 90 minutes.
What is Asteroid?
Asteroids, sometimes called minor planets, are rocky, airless remnants left over from the early
formation of our solar system about 4.6 billion years ago.
The current known asteroid count is: 1,299,621.
Most of this ancient space rubble can be found orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter within the main asteroid belt. Asteroids range in size from Vesta - the largest at about 329 miles (530 kilometers) in diameter - to bodies that are less than 33 feet (10 meters) across. The total mass of all the asteroids combined is less than that of Earth's Moon.
Most of this ancient space rubble can be found orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter within the main asteroid belt. Asteroids range in size from Vesta - the largest at about 329 miles (530 kilometers) in diameter - to bodies that are less than 33 feet (10 meters) across. The total mass of all the asteroids combined is less than that of Earth's Moon.
101955 Bennu
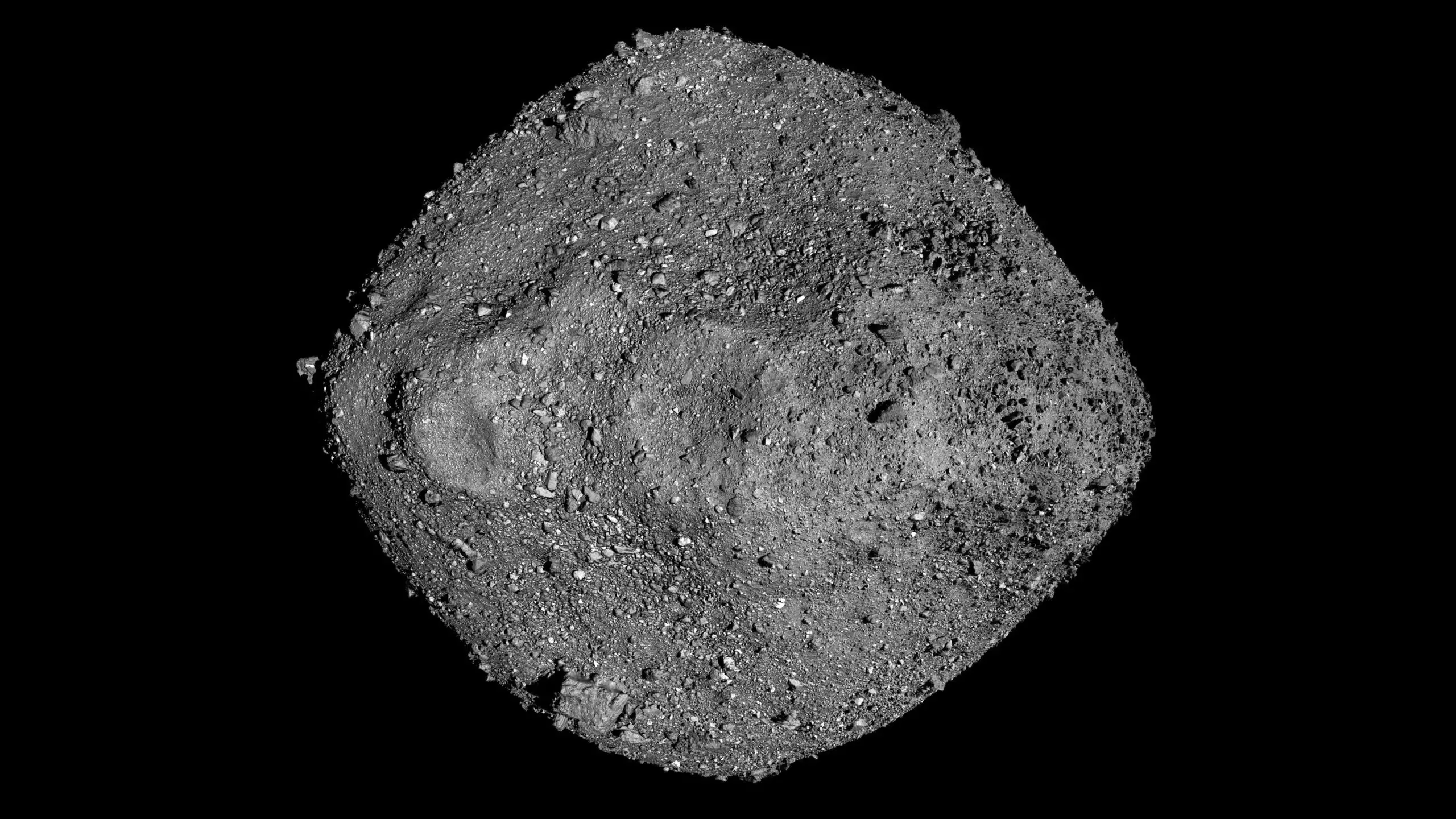

- Discovered - September 11, 1999
- Type - B-Type Asteroid
- Diameter - About 1,614 feet (492 meters)
- Orbital Period - 1.2 Earth Years
- Length of Day - 4.288 hours
- Mass - 85.5 million tons (77.6 million metric tons)
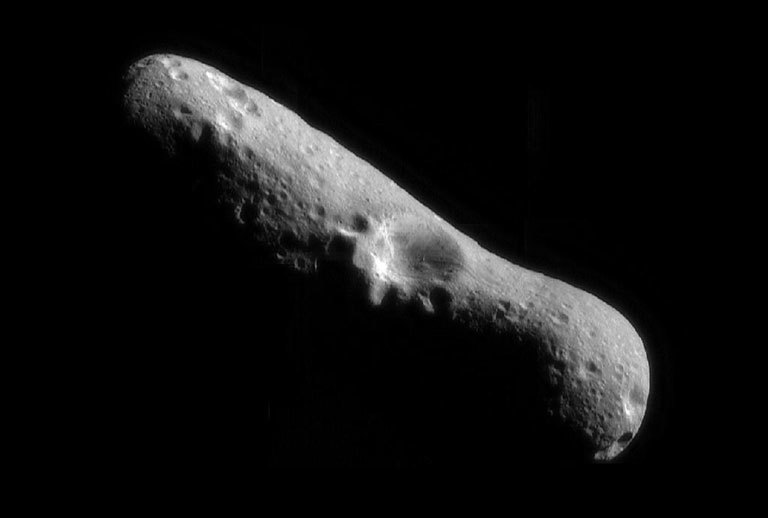
433 Eros
- The NEAR spacecraft first flew by Eros on Dec. 23, 1998, at a distance of about 2,400 miles (about 3,800 kilometers) and found that the asteroid was smaller than expected and had two medium-sized craters, a long surface ridge, and a density similar to that of Earth's crust.
- NamesakeIn a break with tradition at the time, the asteroid was given a male name: Eros, son of Mercury and Venus and god of love in Greek mythology.

What is Space-Craft?
spacecraft, vehicle designed to operate, with or without a crew, in a controlled flight pattern
above Earth's lower atmosphere.
Most spacecraft are not self-propelled; they depend on the initial velocity provided by a launch vehicle, which separates from the spacecraft when its task is done.
Most spacecraft are not self-propelled; they depend on the initial velocity provided by a launch vehicle, which separates from the spacecraft when its task is done.
Sputnik 3
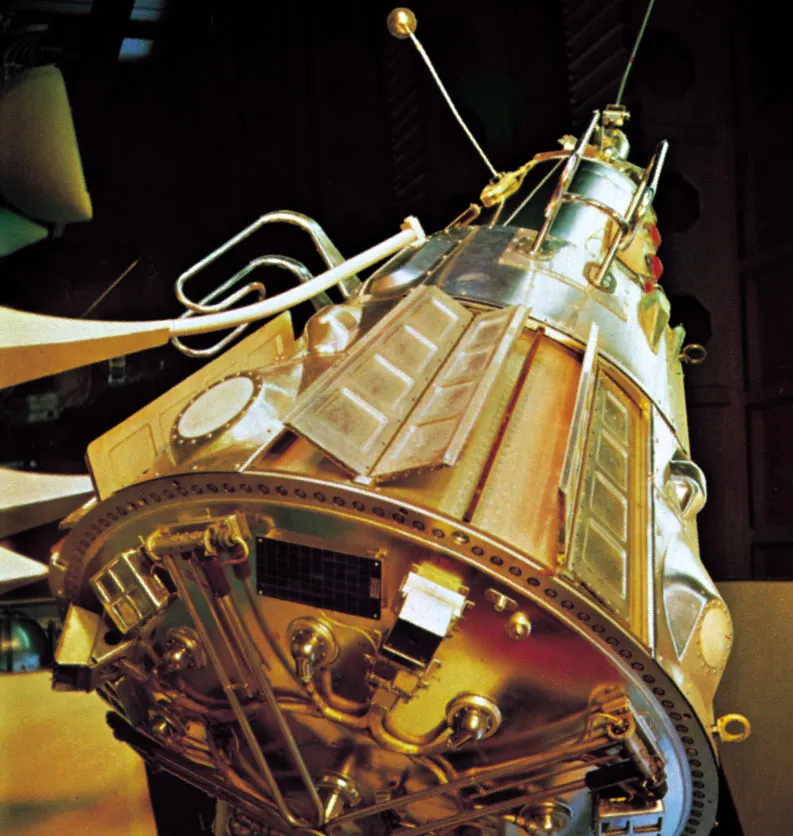
- Sputnik 3, the first multipurpose space-science satellite placed in orbit. Launched May 15, 1958, by the Soviet Union.
- It made and transmitted measurements of the pressure and composition of Earth's upper atmosphere.
- The concentration of charged particles, and the influx of primary cosmic rays.
What is Probe?
A probe is a spacecraft that travels through space to collect science information. Probes do not
have astronauts. Probes send data back to Earth for scientists to study.
Juno

- On August 5, 2011, NASA’s Juno spacecraft embarked on a 5-year journey to our solar system's largest planet - the gas giant Jupiter.
- Its mission: to probe beneath the planet's dense clouds and answer questions about the origin and evolution of Jupiter, our solar system, and giant planets in general across the cosmos.
- Juno arrived at Jupiter on July 4, 2016, after a 5-year, 1.7-billion-mile journey, and settled into a 53-day polar orbit stretching from just above Jupiter’s cloud tops to the outer reaches of the Jovian magnetosphere.
